Internet speed plays a significant role in our day-to-day lives in the linked society we now live in. From viewing high-definition films to working from home, a fast and dependable internet connection is required. However, internet speeds vary greatly throughout the globe. This article will look at the global internet speed extremes, including which nations have the fastest and slowest connections, what causes these discrepancies, and what they signify for individuals and civilizations. ExpressVPN’s internet speed overview highlights the fastest and slowest speeds around the world.
Lets dive in.
Contents
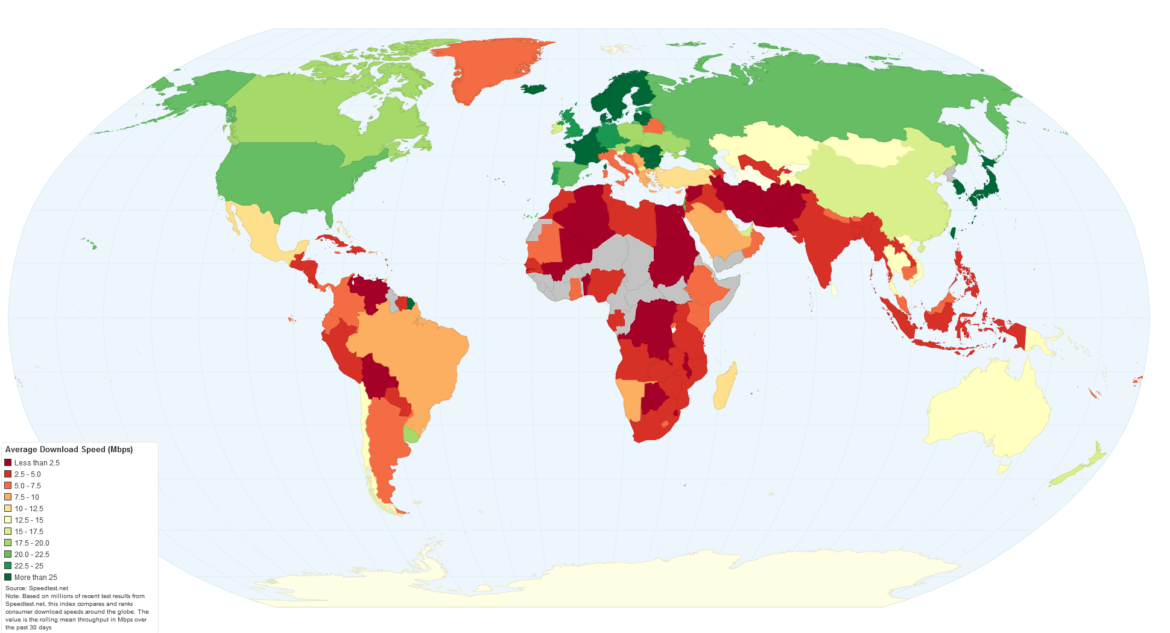
The Fastest Internet Speeds
Monaco: Monaco, a self-contained city-state on the French Riviera, has the world’s fastest average broadband internet speed. With an average speed of 319.59 Mbps, this little principality is at the core of global communication. Monaco’s residents and companies benefit from lightning-fast internet connections as the government invests in modern infrastructure and technology. This streamlines online transactions and encourages innovation.
Singapore: Singapore, which is not far behind Monaco, has emerged as the global leader in internet speed. With an average internet speed of around 300.83 Mbps, this Southeast Asian city-state has established itself as a technological powerhouse. Singapore’s government has made significant expenditures in establishing a robust digital infrastructure, including a nationwide fibre-optic network, to provide residents with ultra-fast internet connections. Singapore’s high-speed internet has assisted the growth of industries such as e-commerce, fintech, and digital services, contributing to the country’s economic prosperity.
Chile: Chile, nestled between the Pacific Ocean and the Andes Mountains, astounds the globe with an average internet speed of roughly 298.5 Mbps. In recent years, the government has made significant progress, investing in fibre-optic networks and other innovative technology to improve access throughout its enormous region. Chile’s dedication to closing the digital gap has resulted in better access to high-speed internet for its population, allowing them to capitalise on the digital economy and enjoy uninterrupted online services.
The Slowest Internet Speeds
Turkmenistan: The world’s slowest average internet speed is currently in Turkmenistan, a country in Central Asia bordered by Iran and Afghanistan. With an average speed of just 0.50 Mbps, the nation confronts enormous hurdles in delivering dependable and fast internet access to its residents. Lack of infrastructure investment, stringent government regulations, and a lack of competition in the telecom sector all contribute to Turkmenistan’s slow internet connections. The sluggish connection impedes the country’s advancement in a variety of areas, including education and healthcare, as well as e-commerce and digital innovation.
Yemen: Some of the slowest internet speeds in the world are in places like Yemen, where the average speed is less than 0.68 Mbps. Political turmoil and a lack of money have made it hard to build infrastructure, making it hard for people to use simple online services. Because of ongoing battles and a lack of funding, these areas have a hard time getting better connections.
Ethiopia: Ethiopia is in the Horn of Africa, which makes it hard for the country to get its people high-speed internet. With an average internet speed of about 1.20 Mbps, the country is not as connected as other countries around the world. Ethiopia’s attempts to expand the internet are hard to do because people don’t have enough access to power, there aren’t enough phones, and there are physical hurdles. But recently, the government has taken steps to improve connections, such as opening up the internet market and putting in place fibre-optic networks. The goal of these attempts is to close the digital gap and help the economy grow.
Implications and Future Considerations

Individuals and organisations are both affected by different internet speeds. Fast, secure internet access is critical for economic development, education, healthcare, and social interactions. Fast internet connections provide countries with an advantage in digital innovation, e-commerce, and working from home, which helps their economies flourish and gives their people more opportunities.
Countries with slower internet connections, on the other hand, have difficulty accessing online resources, participating in the global digital economy, and utilising digital services. This digital divide exacerbates social and economic disparities, delays growth, and restricts people’s and communities’ alternatives.
Everyone must work together to narrow the gap in internet speeds throughout the globe. Governments and businesses should prioritise investments in digital infrastructure, particularly in underserved regions. Policies that promote competition, fresh ideas, and cheap costs may help individuals connect to the internet at high speeds.
Programmes to develop digital knowledge and skills are also vital so that individuals can fully use rapid internet connections. The governmental and corporate sectors, as well as the private sector and foreign organisations, may work together to address challenges and ensure that everyone has equal access to fast internet.
Conclusion
There are big differences in Internet speeds around the world. Some countries have connections that are as fast as lightning, while others have less equipment and slower speeds. These differences are a result of things like advancements in technology, infrastructure improvements, government security, and physical barriers.
Getting rid of the digital gap is important for world growth because everyone should have the same access to high-speed internet. Improving facilities, getting more money, and teaching people how to use technology are all important ways to close this gap and make sure that everyone can enjoy the benefits of a fast and stable internet link.
As technology keeps getting better, governments, organisations, and people need to work together to close the digital gap and make the future more united and open for everyone. By trying to give everyone access to fast internet, we can open up new possibilities, encourage creativity, and make the world a better place.